 | |
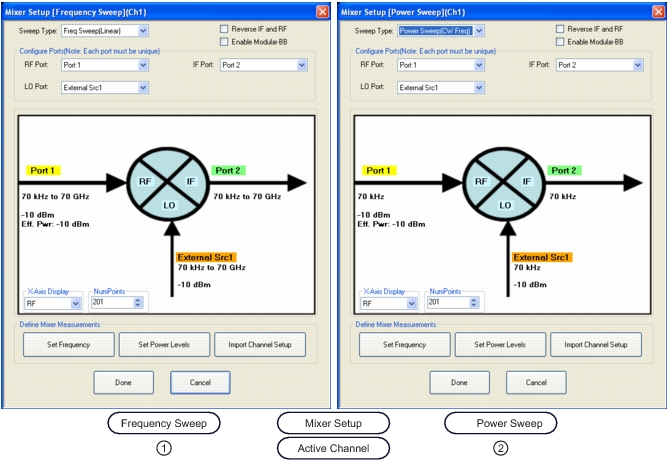
1. On left, MIXER SETUP (FREQUENCY SWEEP). | 2. On right, MIXER SETUP (POWER SWEEP). |
 | |
1. On left, MIXER SETUP (FREQUENCY SWEEP). | 2. On right, MIXER SETUP (POWER SWEEP). |
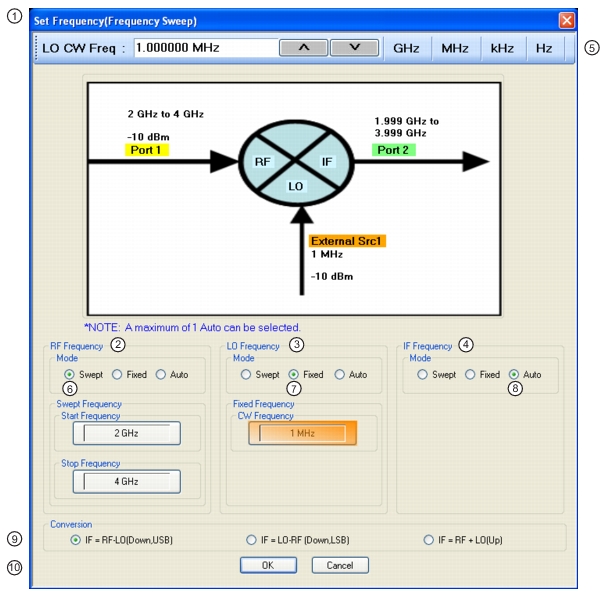 | |
1. SET FREQUENCY (FREQUENCY SWEEP) Wizard Dialog Box. 2. RF Frequency mode and value area. 3. LO Frequency mode and value area. 4. IF Frequency mode and value area. 5. Frequency input field toolbar. The label changes depending whether RF, IF, or LO are selected. 6. Mode set as Swept. Any combination of the RF, IF, and LO ports can be set as Swept. When selected, Start and Stop Frequency fields appear. | 7. Mode set as Fixed. Any combination of the RF, IF, and LO ports can be set as Fixed. When selected, a CW Frequency field appears. 8. Mode set as Auto. Only one of the three ports can be set as Auto. If selected, the instrument determines the frequency settings based on the other two values and the Conversion type setting. 9. Conversion setting. Changes based on whether RF is input or output. 10. Dialog box control buttons. |
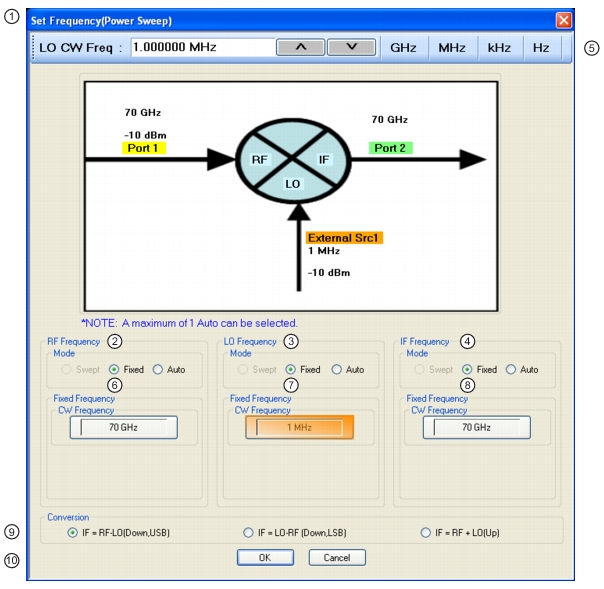 | |
1. SET FREQUENCY (POWER SWEEP) Dialog Box. 2. RF Frequency mode and value area. 3. LO Frequency mode and value area. 4. IF Frequency mode and value area. 5. Frequency input field toolbar. The label changes depending whether RF, IF, or LO are selected. 6. RF Mode setting can only be Fixed or Auto. Only one mixer port can be Auto. If fixed, RF CW frequency is input in field below. | 7. LO Mode setting can only be Fixed or Auto. Only one mixer port can be Auto. LO CW frequency is input in field below. 8. IF Mode setting can only be Fixed or Auto. Only one mixer port can be Auto. IF CW frequency is input in field below. 9. Conversion setting. Changes based on whether RF is input or output. If RF is input, equations show conversion calculations for IF. If IF is input, equations show conversion calculations for RF. 10. Dialog box control buttons. |
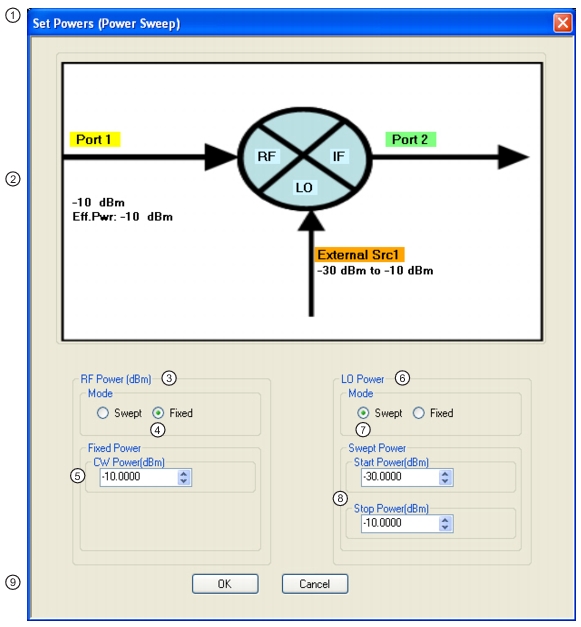 | |
1. SET POWERS (POWER SWEEP) Wizard Dialog Box 2. Mixer Schematic – Port assignments and power levels are updated automatically. 3. RF Power (dBm) controls. 4. RF Power Mode set as Fixed with option of Swept. 5. RF Power CW Power input field | 6. LO Power controls 7. Mode set as Swept with option of Fixed. 8. Swept start and stop power input fields. 9. Dialog box control buttons. |