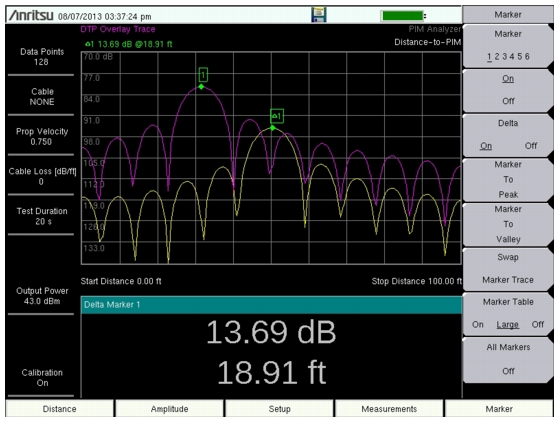
Trace Overlay is a feature allowing comparison in the field between a Distance‑to‑PIM trace that is active and a Distance‑to‑PIM trace that is saved in memory (an overlay trace). This is useful for determining (at a site) the distance between an unknown PIM source and a known PIM source. For example, placing a bag of steel wool on an antenna radome and performing a Distance‑to‑PIM measurement will generate a high magnitude “PIM Marker” at the location of the antenna aperture. Place this trace into memory (overlay trace), and then measure Distance‑to‑PIM again with the steel wool removed. This active trace shows the distance to the actual PIM sources at the site. The distance between the peak of the active trace (site PIM) and the overlay trace (PIM Marker) shows how far in front of the antenna the PIM source is located if the distance value is positive. If the distance value is negative, then the unknown PIM source is before the antenna, inside the feed system. Refer to
Trace.
After you leave the site, Anritsu Line Sweep Tools (LST) also provides a method to overlay multiple DTP results.
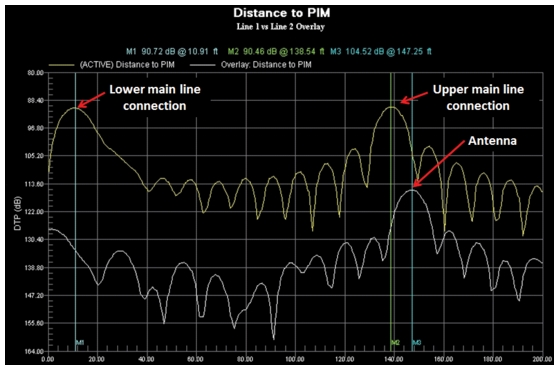
Figure: Distance‑to‑PIM Overlay of Sector Main and Diversity Paths shows an overlay of two DTP measurements from the main receive path and the diversity receive path of a sector. One line has very good PIM performance, but the other line needs repair. Using the good line (lower trace) as a reference, you can clearly see that the PIM problems on the bad line are 11 feet away from the radio at the main line connection and 11 feet behind the antenna at the top (also at a main line connection). LST also could be used to report site improvements by creating an overlay of saved measurements that are taken before and after repairs.