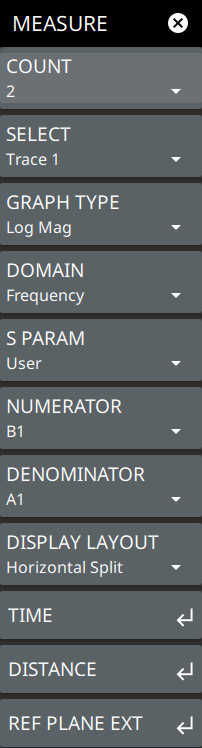
 | COUNT Selects the number of trace count. Maximum of 4 traces are supported. SELECT Selects the number of active traces to be displayed on the sweep window. GRAPH TYPE Selects any of the following graph types for an active trace: • Log Mag: Log magnitude is used to measure return loss at Port 1 (or Port 2), or gain or loss in a DUT that is connected between Port 1 and Port 2. • SWR: Standing wave ratio (SWR) is used to measure the reflection (S11) from the DUT input port or output port. • Phase: Use the Phase or Unwrapped Phase measurement to display the phase in degrees of Sxy. The Phase measurement is contained within a vertical scale of ±180º, whereas the unwrapped phase displays the linear phase without wrapping it at the 180 degrees transitions. • Smith: Smith chart is a plot of input and output impedance of the DUT using S11 versus frequency. • Group Delay: Group Delay graph type is a measure of the time delay of the signals that are propagating through the DUT versus frequency (using S21). Group delay is a good measure of phase distortion through the DUT. Group delay is equal to rate of change of phase over a specified frequency aperture. • Real: Real graph type denotes real part of the complex S-Parameter Sxy. • Imaginary: Imaginary graph type denotes imaginary part of the complex S-Parameter Sxy. • Imaginary Imp: An imaginary graph in the context of a Vector Network Analyzer (VNA) typically represents the imaginary component of complex impedance or reflection coefficients (S-parameters) as a function of frequency. This type of graph is useful for analyzing how the reactive components (inductive and capacitive) of a device under test (DUT) behave over a specified frequency range. • Inverted Smith: An inverted Smith chart is a variation of the traditional Smith chart used in RF and microwave engineering for displaying complex impedance and reflection coefficients in a more intuitive way, particularly for certain types of analysis. • Log Mag/2: Measures 1-port cable loss, using S11 to account for the round trip signal path through the cable. When using reflection data to measure cable loss, the end of the cable must be shorted or must be a perfect open. • Linear Polar: Linear polar graph typically refers to a graphical representation of complex impedance or reflection coefficients (S-parameters) in a polar coordinate system. This representation is useful for visualizing how the impedance of a device changes with frequency or how it behaves in response to varying input signals. • Log Polar: A log polar graph is a specialized type of graphical representation used in Vector Network Analyzers (VNAs) to display the magnitude and phase of S-parameters, particularly useful for analyzing wide-ranging values of impedance or reflection coefficients across a frequency spectrum. • Unwrapped Phase: The unwrapped Phase graph removes the wrapping and plots the phase linearly. Unwrapped phase is obtained by counting the number of transitions of the phase measurement. • Linear Mag: A linear magnitude graph in a Vector Network Analyzer (VNA) is a straightforward representation used to visualize the magnitude of S-parameters (scattering parameters) over a specified frequency range. This type of graph is particularly useful for assessing the performance of RF and microwave components, such as antennas, filters, and amplifiers. |
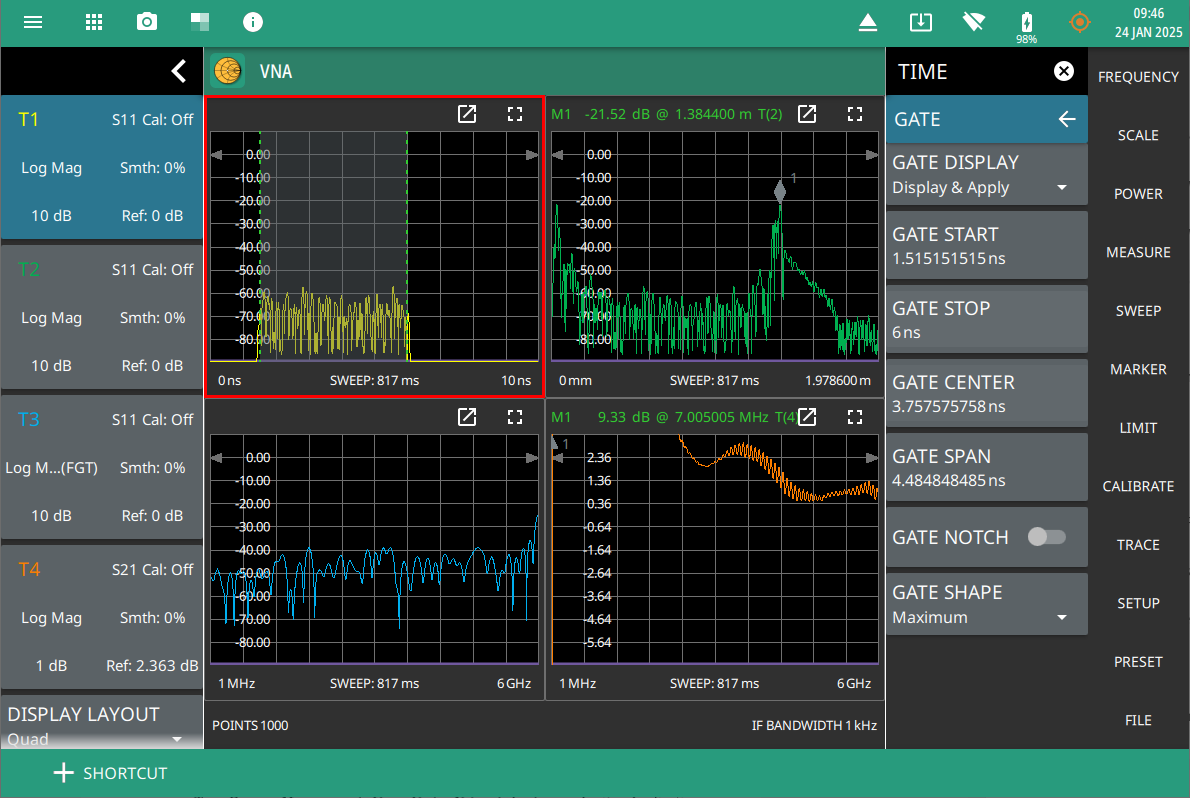
• Z-Magnitude: A Z-magnitude graph in a Vector Network Analyzer (VNA) displays the magnitude of impedance (Z) as a function of frequency. This type of graph is useful for analyzing how the impedance of a device under test (DUT) varies with frequency, providing insights into the performance characteristics of RF and microwave components. DOMAIN Selects any one of the following domain options: • Frequency: Sets the x-axis of the active trace to frequency domain. • Time: Sets the x-axis of the active trace to time domain. Note that time domain is available when Time Domain with Gating Option 2 is installed. • Distance: Sets the x-axis of the active trace to distance domain. Note that distance domain is available when Time Domain with Gating, Option 2 is installed. • Freq Gate: Sets the x-axis of the active trace to frequency gate domain. Note that frequency gate domain is available when Time Domain with Gating Option 2 is installed. Note that status panel indicates ‘(FGT)’ next to the selected graph type only if Domain is set of Freq Gate. S PARAM Selects any one of the following S-Parameter options: • S11: Set the measurement to S11 Forward Reflection (receive at Port 1, transmit from Port 1). • S21: Sets the measurement to S21 Forward Transmission (receive at Port 2, transmit from Port 1). • User: Sets the user-defined S-Parameters by choosing a combination of available numerator and denominator values. For example, if numerator is set as B1 and denominator is set as A1 the instrument measures the S11 forward reflection. See Table: User-Defined Numerator/Denominator Combinations. • S21 (Ext. Sens): Forward Transmission represents the measurement in which the signal leaves port 1 and is transmitted to Port 2. In this case an external USB power sensor is used as Port 2. NUMERATOR Selects any of one of the following as numerator: • A1: Denotes the reference signal from source Port 1. • B1: Denotes the received power into Port 1. • B2: Denotes the received power into Port 2. • One: Denotes the number 1 as the numerator. DENOMINATOR Selects any of one of the following as numerator: • A1: Denotes the reference signal from source Port 1. • B1: Denotes the received power into Port 1. • B2: Denotes the received power into Port 2. • One: Denotes the number 1 as the denominator. DISPLAY LAYOUT Selects any of the following display layouts: • Single: Displays the active trace at full size in the sweep window. • Horizontal Split: Displays 2 active traces in the sweep window, with the sweep window divided horizontally into 2 equal rectangles. • Vertical Split: Displays 2 active traces in the sweep window, with the sweep window divided vertically into 2 equal rectangles. • Horizontal Triple: Displays 3 traces in the sweep window, with the sweep window divided horizontally and vertically so that 2 equal rectangles share the lower half of the window, and one wide rectangle occupies the upper half of the window. • Vertical Triple: Displays 3 traces in the sweep window, with the sweep window divided horizontally and vertically so that 2 equal rectangles share the left half of the window, and one wide rectangle occupies the right half of the window. • Quad: Displays 4 traces in the sweep window, with the sweep window divided horizontally and vertically into 4 equal rectangles. | |
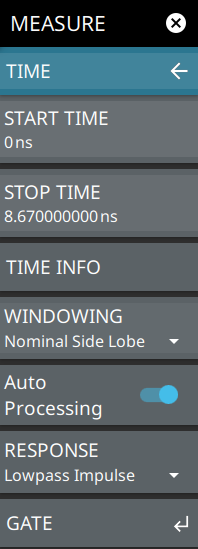
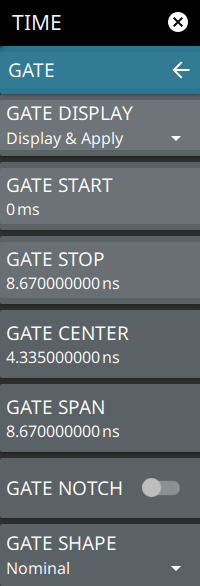
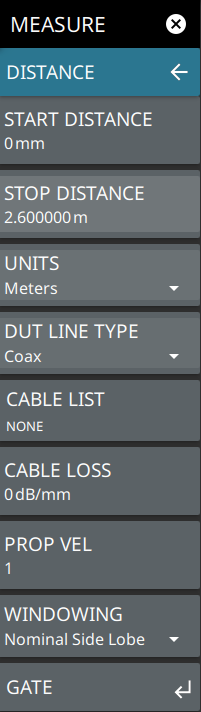
TIME Opens the TIME Menu. DISTANCE Opens the DISTANCE Menu. REF PLANE EXT Opens the REF PLANE EXT Menu. |